- GIS and Spatial Analysis
- GIS and Web Gis 2.0
GIS & Web Gis 2.0 Principles and Overview
What is a G.I.S.

A geographic information system (GIS) is a computer-based tool for mapping and analyzing things that exist and events that happen on earth.
GIS technology integrates common database operations such as query and statistical analysis with the unique visualization and geographic analysis benefits offered by maps.These abilities distinguish GIS from other information systems and make it valuable to a wide range of public and private enterprises for explaining events, predicting outcomes, and planning strategies.
The state of the art for managing territorial information data.
A wide spreading technology for land use planning, and assessing environmental phenomena.
A “must” tool for facing the decision making processes towards sustainable development.
GIS is a technology that
visualize,
manages,
analyzes,
and share geographic knowledge
& spatial data
Data from most sciences can be analyzed “spatially”: estimates are that 80% of all data has a spatial component
Applications of GIS
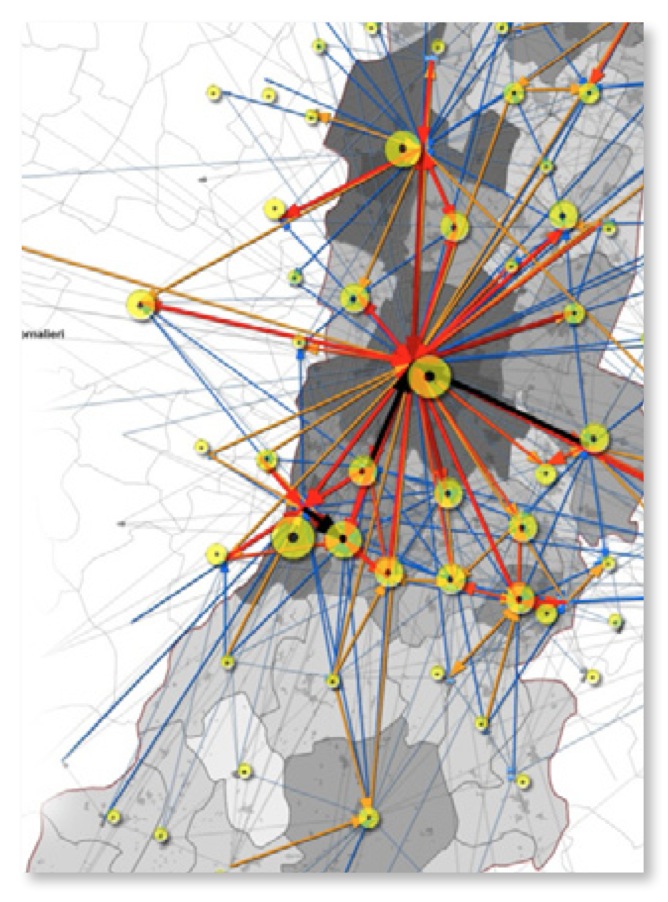
GIS is used (might and should be used) wherever Spatial Data Analysis is needed, such as ...
Emergency Services – Fire & Police
Environmental – Monitoring & Modeling
Business – Site Location, Delivery Systems
Industry – Transportation, Communication, Mining, Pipelines, Healthcare
Politics and Government – Local, State, Federal, Military
Education Research, Teaching Tool,
Administration – Land Use Planning, Tributes, eGovernment
and so on ...
GIS & WEB 2.0

In recent years GIS technologies, initially based on proprietary desktop applications (commercial), have evolved and benefited from new technologies in the Web and especially the Web 2.0 paradigm.
The advent of Ajax development techniques, Google Maps and the availability of its public API has resulted in the evolution of Web GIS and Web GIS 2.0 applications development, based on "opensource" tools and programming frameworks (HTML5, CSS3, Javascript JQuery &, PHP, Drupal, etc.).
Today it is possibile and appropriate to conceive and develop WEB 2.0 GIS: GIS on the web do not serve only to publish data in its own possession, but let you capture, collect, edit and publish data coming from the public and the applications’ users themselves.
Web maps and Web GIS applications become increasingly rich, dynamic and pervasive, and integrate as significant components of more evolved Web 2.0 solutions, in any scope: mashups, user-generated content, mobile applications, social networks, promotion of "big data" and business intelligence applications in real time.